 Overview
Overviewhammertoes is the general term used to describe an abnormal contraction or "buckling" of the toe because of a partial or complete dislocation of one of the joints of the toe or the joint where the toe joins with the rest of the foot. As the toe becomes deformed, it rubs against the shoe and the irritation causes the body to build up more and thicker skin to help protect the area. The common name for the thicker skin is a corn.
Causes
Hammer toe usually affects the second toe. However, it may also affect the other toes. The toe moves into a claw-like position. The most common cause of hammer toe is wearing short, narrow shoes that are too tight. The toe is forced into a bent position. Muscles and tendons in the toe tighten and become shorter. Hammer toe is more likely to occur in women who wear shoes that hammertoe do not fit well or have high heels and children who keep wearing shoes they have outgrown. The condition may be present at birth (congenital) or develop over time. In rare cases, all of the toes are affected. This may be caused by a problem with the nerves or spinal cord.
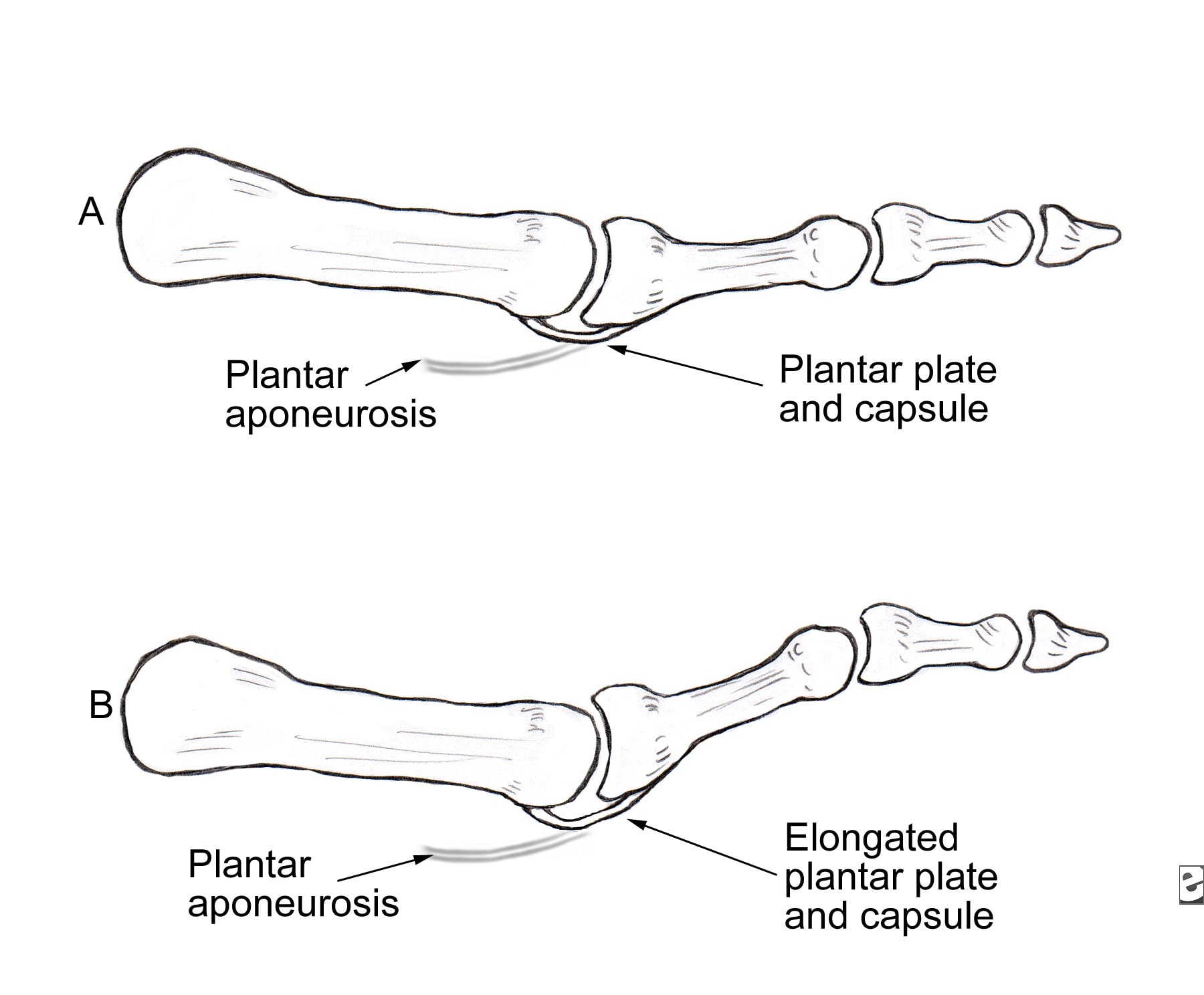 Symptoms
SymptomsA hammer toe may be painful, especially when irritated by a shoe. All four toe conditions may cause cramps in the toes, foot and leg due to the abnormal function of the tendons in the foot. If a mallet toe has occurred, you are likely to suffer from a corn at the end of the toe. A hammertoe may cause a corn on the top of the toe. Infections and ulcers can also occur. In severe cases a mallet toe, trigger toe, claw toe or a hammer toe may create a downward pressure on the foot, which can result in hard skin and corns on the soles of the feet.
Diagnosis
The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
A number of approaches can be undertaken to the manage a hammer toe. It is important that any footwear advice is followed. The correct amount of space in the toe box will allow room for the toes to function without excessive pressure. If a corn is present, this will need to be treated. If the toe is still flexible, it may be possible to use splints or tape to try and correct the toe. Without correct fitting footwear, this is often unsuccessful. Padding is often used to get pressure off the toe to help the symptoms. If conservative treatment is unsuccessful at helping the symptoms, surgery is often a good option.
Surgical Treatment
The deformity is corrected in a variety of ways. There are actually a large number of procedures. The simplest procedure would involve a Tenotomy, the cutting of the tendon causing the deformity or a Tendon Lengthening procedure. These procedures are infrequently done, though, as the structural deformity (the arthritis and joint adaptation) is not addressed with these surgeries. Other soft-tissue procedures involve rebalancing the tendons around the joint. There are several techniques to do this, but the most common is probably the Girdlestone-Taylor procedure, which involves rerouting the tendons on the bottom of the toe up and over the toe where it sticks up, so that the tendon helps pull the toe downwards into proper alignment.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
