Overview
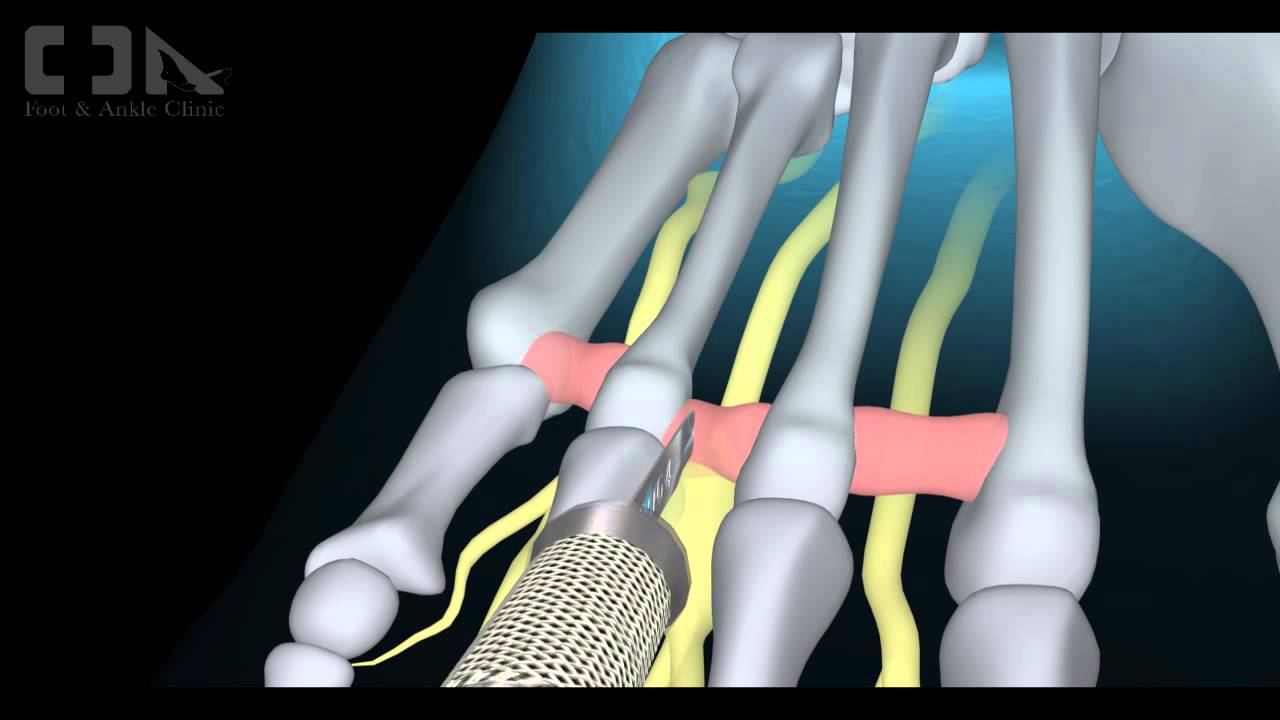 Morton?s Neuroma is a common foot condition characterized by pain and swelling in the ball of the foot, between the third and fourth toes. It?s caused by bones in your feet squeezing a nerve. Symptoms include a sharp, burning pain and possibly separation between the affected toes.
Morton?s Neuroma is a common foot condition characterized by pain and swelling in the ball of the foot, between the third and fourth toes. It?s caused by bones in your feet squeezing a nerve. Symptoms include a sharp, burning pain and possibly separation between the affected toes.
Causes
A Morton?s Neuroma are a result of complex biomechanical changes that occur in your feet. There are a number of theories as to the exact cause of the scarring and thickening, but it basically boils down to overload of the tissue structure. The body lays down scar tissue to try to protect the overloaded structure. Tight-fitting shoes may exacerbate a Morton?s Neuroma. Shoes such as high heels and shoes with tight toe boxes (eg womens fashion shoes and cowboy boots) are particularly damaging to the toes. These shoes have a sloping foot bed and a narrow toe box. The slope causes the front of the foot to bear your weight. The angle of the toe box then squeezes your toes together. Footwear is not the only cause of a Morton?s Neuroma. Injuries to the foot can also be a factor in developing the condition by changing your foot biomechanics. Poor foot arch control leading to flat feet or foot overpronation does make you biomechanically susceptible to a neuroma.
Symptoms
Symptoms of interdigital neuroma typically manifest as a sharp, burning or tingling sensation in the forefoot. The pain radiates toward the lesser toes and is aggravated by shoe wear. The pain is relieved when the shoe is removed and the forefoot is massaged. Sometimes the symptoms involve specific toes.
Diagnosis
To diagnose Morton's neuroma the podiatrist commonly palpates the area to elicit pain, squeezing the toes from the side. Next he or she may try to feel the neuroma by pressing a thumb into the third interspace. The podiatrist then tries to elicit Mulder's sign, by palpating the affected interspace with one hand and squeezing the entire foot at the same time with the other hand. In many cases of Morton's neuroma, this causes an audible click, known as Mulder's sign. An x-ray should be taken to ensure that there is not a fracture. X-rays also can be used to examine the joints and bone density, ruling out arthritis (particularly rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis).
Non Surgical Treatment
Orthotics and corticosteroid injections are widely used conservative treatments for Morton?s neuroma. In addition to traditional orthotic arch supports, a small foam or fabric pad may be positioned under the space between the two affected metatarsals, immediately behind the bone ends. This pad helps to splay the metatarsal bones and create more space for the nerve so as to relieve pressure and irritation. It may however also elicit mild uncomfortable sensations of its own, such as the feeling of having an awkward object under one's foot. Corticosteroid injections can relieve inflammation in some patients and help to end the symptoms. For some patients, however, the inflammation and pain recur after some weeks or months, and corticosteroids can only be used a limited number of times because they cause progressive degeneration of ligamentous and tendinous tissues.
Surgical Treatment
The ultimate success of a Morton?s neuroma treated surgically can be variable. In cases where the underlying problem is only an irritated nerve (a true Morton?s neuroma), then surgery will probably be curative (although it may take a few months for the foot to fully heal). But in many cases, forefoot pain is more complex. There may be an irritated nerve or two causing pain, but the real problem is often excessive loading of the lesser metatarsals. The generic term for this condition is metatarsalgia. When considering surgery, identifying and addressing these problems may lead to a better end result.
 Morton?s Neuroma is a common foot condition characterized by pain and swelling in the ball of the foot, between the third and fourth toes. It?s caused by bones in your feet squeezing a nerve. Symptoms include a sharp, burning pain and possibly separation between the affected toes.
Morton?s Neuroma is a common foot condition characterized by pain and swelling in the ball of the foot, between the third and fourth toes. It?s caused by bones in your feet squeezing a nerve. Symptoms include a sharp, burning pain and possibly separation between the affected toes.Causes
A Morton?s Neuroma are a result of complex biomechanical changes that occur in your feet. There are a number of theories as to the exact cause of the scarring and thickening, but it basically boils down to overload of the tissue structure. The body lays down scar tissue to try to protect the overloaded structure. Tight-fitting shoes may exacerbate a Morton?s Neuroma. Shoes such as high heels and shoes with tight toe boxes (eg womens fashion shoes and cowboy boots) are particularly damaging to the toes. These shoes have a sloping foot bed and a narrow toe box. The slope causes the front of the foot to bear your weight. The angle of the toe box then squeezes your toes together. Footwear is not the only cause of a Morton?s Neuroma. Injuries to the foot can also be a factor in developing the condition by changing your foot biomechanics. Poor foot arch control leading to flat feet or foot overpronation does make you biomechanically susceptible to a neuroma.
Symptoms
Symptoms of interdigital neuroma typically manifest as a sharp, burning or tingling sensation in the forefoot. The pain radiates toward the lesser toes and is aggravated by shoe wear. The pain is relieved when the shoe is removed and the forefoot is massaged. Sometimes the symptoms involve specific toes.
Diagnosis
To diagnose Morton's neuroma the podiatrist commonly palpates the area to elicit pain, squeezing the toes from the side. Next he or she may try to feel the neuroma by pressing a thumb into the third interspace. The podiatrist then tries to elicit Mulder's sign, by palpating the affected interspace with one hand and squeezing the entire foot at the same time with the other hand. In many cases of Morton's neuroma, this causes an audible click, known as Mulder's sign. An x-ray should be taken to ensure that there is not a fracture. X-rays also can be used to examine the joints and bone density, ruling out arthritis (particularly rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis).
Non Surgical Treatment
Orthotics and corticosteroid injections are widely used conservative treatments for Morton?s neuroma. In addition to traditional orthotic arch supports, a small foam or fabric pad may be positioned under the space between the two affected metatarsals, immediately behind the bone ends. This pad helps to splay the metatarsal bones and create more space for the nerve so as to relieve pressure and irritation. It may however also elicit mild uncomfortable sensations of its own, such as the feeling of having an awkward object under one's foot. Corticosteroid injections can relieve inflammation in some patients and help to end the symptoms. For some patients, however, the inflammation and pain recur after some weeks or months, and corticosteroids can only be used a limited number of times because they cause progressive degeneration of ligamentous and tendinous tissues.

Surgical Treatment
The ultimate success of a Morton?s neuroma treated surgically can be variable. In cases where the underlying problem is only an irritated nerve (a true Morton?s neuroma), then surgery will probably be curative (although it may take a few months for the foot to fully heal). But in many cases, forefoot pain is more complex. There may be an irritated nerve or two causing pain, but the real problem is often excessive loading of the lesser metatarsals. The generic term for this condition is metatarsalgia. When considering surgery, identifying and addressing these problems may lead to a better end result.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
